1
1111 W. 35th Street, Chicago, IL 60609 USA • www.tripplite.com/support
Owner’s Manual
Console Server Management Switch
Models:
B096-016 / B096-032 / B096-048
Console Server with PowerAlert
Model:
B092-016
Console Server
Models:
B095-004-1E / B095-003-1E-M / B094-008-2E-M-F / B094-008-2E-V
Copyright © 2015 Tripp Lite. All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PROTECT YOUR INVESTMENT!
Register your product for quicker service and ultimate peace of mind.
You could also win an ISOBAR6ULTRA surge protector—a $100 value!
www.tripplite.com/warranty
Оглавление инструкции
- Страница 1 из 274
Owner’s Manual Console Server Management Switch Models: B096-016 / B096-032 / B096-048 Console Server with PowerAlert Model: B092-016 Console Server Models: B095-004-1E / B095-003-1E-M / B094-008-2E-M-F / B094-008-2E-V PROTECT YOUR INVESTMENT! Register your product for quicker service and ultimate - Страница 2 из 274
FCC Information, Class A This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired - Страница 3 из 274
Table of Contents Introduction 10 Installation 14 Initial System Configuration 19 Serial Port, Device & User Configuration 38 2.1 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.1.4 2.2 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 3.1 3.1.1 3.1.2 3.1.3 3.2 3.2.1 3.3 3.3.1 3.3.2 3.4 3.4.1 3.5 3.5.1 3.5.2 3.5.3 3.6 3.6.1 3.6.2 3.6.3 3.6.4 - Страница 4 из 274
Table of Contents 4.5 4.6 4.6.1 4.6.2 4.6.3 4.6.4 4.7 4.7.1 4.7.2 4.7.3 4.7.4 4.8 4.9 4.9.1 4.10 4.10.1 4.10.2 4.10.3 4.11 4.11.1 4.11.2 4.11.3 4.12 4.12.1 4.12.2 4.12.3 4.12.4 4.12.5 4.12.6 Trusted Networks Serial Port Cascading Automatically generate and upload SSH keys Manually generate and - Страница 5 из 274
Table of Contents 5.7 5.7.1 5.7.2 5.7.3 Cellular Operation OOB access set up Cellular failover setup Cellular routing 88 88 89 89 Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.1 6.2 6.2.1 6.2.2 6.2.3 6.2.4 6.2.5 6.2.6 6.2.7 6.2.8 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.8.1 6.8.2 6.9 6.9.1 6.9.2 6.10 6.10.1 6.10.2 - Страница 6 из 274
Table of Contents 7.2 7.2.1 7.2.2 7.2.3 7.2.4 7.2.5 7.2.6 7.2.7 7.2.8 7.2.9 7.2.10 7.2.11 7.2.12 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 Trigger and Resolve Actions Send Email on Trigger Send SMS on Trigger Perform RPC Action on Trigger Run Custom Script on Trigger Send SNMP Trap on Trigger Send Nagios Event on - Страница 7 из 274
Table of Contents Nagios Integration 160 System Management 173 Status Reports 179 Management 184 Command Line Configuration 188 10.1 10.2 10.2.1 10.2.2 10.3 10.3.1 10.3.2 10.3.3 10.3.4 10.3.5 10.3.6 10.4 10.4.1 10.4.2 10.4.3 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.5.1 12.5.2 13.1 - Страница 8 из 274
Table of Contents 14.1.8 14.1.9 14.1.10 14.1.11 14.1.12 14.1.13 14.1.14 14.1.15 14.1.16 14.1.17 14.1.18 14.1.19 14.1.20 14.1.21 14.1.22 14.2 UPS Connections RPC Connections Environmental Managed Devices Port Log Alerts SMTP & SMS SNMP Administration IP settings Date & Time settings Dial-in settings - Страница 9 из 274
Table of Contents 15.8 15.8.1 15.8.2 15.8.3 15.8.4 15.9 15.9.1 15.9.2 15.9.3 15.10 15.11 15.12 15.13 15.14 15.14.1 15.14.2 15.14.3 15.14.4 15.14.5 HTTPS Generating an encryption key Generating a self-signed certificate with OpenSSL Installing the key and certificate Launching the HTTPS Server Power - Страница 10 из 274
Chapter 1: Introduction This User Manual is provided to help you get the most from your B096-016 / B096-032 / B096-048 Console Server Management Switch, B092-016 Console Server with PowerAlert or B095-004-1E / B095-003-1E-M / B094-008-2E-M-F / B094-008-2E-V Console Server product. These products - Страница 11 из 274
Chapter 1: Introduction Types of users The Console Server supports two classes of users: I. Administrative users: Those who will be authorized to configure and control the Console Server; and to access and control all the connected devices. These administrative users will be set up as members of - Страница 12 из 274
Chapter 1: Introduction The Console Server runs an embedded Linux operating system. Experienced Linux and UNIX users may prefer to undertake configuration at the command line. As an Administrator you can get command line access by connecting through a terminal emulator or communications program to - Страница 13 из 274
Chapter 1: Introduction Publishing history Date Revision Update details January 2009 0.9 Initial draft February 2009 0.91 Pre-release January 2010 1.01 Add B095-004/003 Console Server and Firmware 3.0.1 features January 2011 2.0 Firmware 3.3.2 features March 2011 2.0.1 Support for additional USB - Страница 14 из 274
Chapter 2: Installation This chapter describes the physical installation of the Console Server hardware and connection to controlled devices 2.1 Models There are a number of Console Server models, each with a different number of network, USB and serial ports and power supplies: Console Server Model - Страница 15 из 274
Chapter 2: Installation 2.1.2 Kit components: B092-016 Console Server with PowerAlert B092-016 Console Server with PowerAlert 2 x Cable UTP Cat5 blue Connector DB9F-RJ45S straight and DB9F-RJ45S cross-over AC power cable Quick Start Guide and CD-ROM • Unpack your Console Server and verify you have - Страница 16 из 274
Chapter 2: Installation 2.1.4 Kit components: B094-008-2E-M-F and B094-008-2E-V Console Server B094-008-2E-M-F 8- port Console Server with dual NIC and modem or B094-008-2E-V 8 -port Console Server with dual NIC and cellular 2 x Cable UTP Cat5 blue Connectors DB9F-RJ45S straight and cross-over - Страница 17 из 274
Chapter 2: Installation 2.2 Power Connection 2.2.1 Power: Console Server Management Switch The B096-048/032/016 Console Server Management Switch has dual universal AC power supplies with auto failover built in. These power supplies each accept AC input voltage between 100 and 240 VAC with a - Страница 18 из 274
Chapter 2: Installation 2.4 Serial Port Connection The RJ45 serial ports are located on the rear of the B092-016 Console Server, on the front of the B096-048/032/016 Console Server and B094-008 Console Server, and on the side panel of the B095-004/003 Console Server. These Console Servers use the - Страница 19 из 274
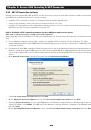
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration This chapter provides step-by-step instructions for the initial configuration of your Console Server and connecting it to your management or operational network. This involves the Administrator: • Activating the Management Console • Changing the Administrator - Страница 20 из 274
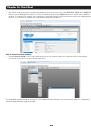
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration Now add a static entry to the ARP table and ping the Console Server to assign the IP address to the console server. In the example below, a Console Server has a MAC Address 00:13:C6:00:02:0F (designated on the label on the bottom of the unit) and we are - Страница 21 из 274
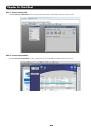
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration A Welcome screen, which lists initial installation configuration steps, will be displayed. These steps are: • Change default administration password (System/Administration page. Refer Chapter 3.2) • Configure the local network settings (System/IP page. Refer - Страница 22 из 274
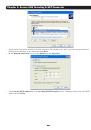
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.2 Administrator Password For security reasons, only the administration user named root can initially log into your Console Server. Only those people who know the root password can access and reconfigure the Console Server itself. However, anyone who - Страница 23 из 274
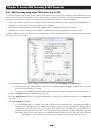
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration • You may now wish to enter a System Name and System Description for the Console Server to give it a unique ID and make it simple to identify Note: The System Name can contain from 1 to 64 alphanumeric characters (however you can also use the special - Страница 24 из 274
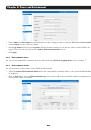
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.3 Network IP Address It is time to enter an IP address for the principal 10/100 LAN port on the Console Server; or enable its DHCP client so that it automatically obtains an IP address from a DHCP server on the network to which it is to be connected. • On - Страница 25 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.3.1 IPv6 configuration By default, the Console Server Ethernet interfaces support IPv. However, they can also be configured for IPv6 operation: • On the System: IP menu select General Settings page and check Enable IPv6 • You will then need to configure the - Страница 26 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.3.2 Dynamic DNS (DDNS) configuration Dynamic DNS (DDNS) enables a Console Server with a dynamically assigned IP address (that may change from time to time) to be located using a fixed host or domain name. • The first step in enabling DDNS is to create an - Страница 27 из 274
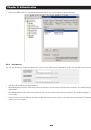
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.4 System Services and Service Access Service Access specifies which access protocols/services can be used to access the Console Server (and connected serial ports). The Administrator can access and configure the Console Server (and connected devices) using - Страница 28 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration The Services Access settings specify which services the Administrator can use over which network interface to access the console server. It also nominates the enabled services that the Administrator and the User can use to connect through the Console Server - Страница 29 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration • The B092-016 Console Server with PowerAlert also presents some additional service and configuration options: VNC The B092-016 Console Server has an internal VNC server. When enabled, it allows remote users to connect to the Console Server and run the - Страница 30 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.4.1 Brute force protection Brute force protection (Micro Fail2ban) temporarily blocks source IPs that show malicious signs, such as too many password failures. This may help mitigate scenarios where the appliance’s network services are exposed to an - Страница 31 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.5 Communications Software You need to configure the access protocols that the communications software on the Administrator and User Computer will use when connecting to the Console Server (and when connecting to serial devices and network hosts which are - Страница 32 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.5.3 SSHTerm Another common communications package that may be useful is SSHTerm. This is an open source package that can be downloaded from http://sourceforge.net/projects/sshtools • To use SSHTerm for an SSH terminal session from a Windows Client, simply - Страница 33 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration 3.6 Management Network Configuration The B096-048/032/016 Console Server Management Switches and B094-008-2E-M-F / B094-008-2E-V Console Server each have an additional network port that can be configured as a Management LAN port or as a failover/ OOB access - Страница 34 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration The management gateway function is now enabled with default firewall and router rules. By default these rules are configured so the Management LAN can only be accessible by SSH port forwarding. This ensures the remote and local connections to Managed Devices - Страница 35 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration The DHCP server also supports pre-assigning IP addresses to be allocated only to specific MAC addresses and reserving IP addresses to be used by connected hosts with fixed IP addresses. To reserve an IP addresses for a particular host: • Click Add in the - Страница 36 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration With bridging enabled: • the Ethernet ports are transparently interconnected at the data link layer (layer 2) • the Ethernet ports are configured collectively using the Network Interface menu • network traffic is forwarded between all Ethernet ports with no - Страница 37 из 274
Chapter 3: Initial System Configuration • Authentication – this is covered in more detail in Chapter 9 • Network Hosts – configuring access to local network connected computers or appliances (hosts) • Configuring Trusted Networks - nominate specific IP addresses that trusted users access from • - Страница 38 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.1 Configuring Serial Ports To configure a serial port you must first set the Common Settings (Chapter 4.1.1) that are to be used for the data connection to that port (e.g. baud rate) and the mode the port is to operate in. Each port can be set - Страница 39 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.1.1 Common Settings There are a number of common settings available for each serial port. These are independent of the mode in which the port is being used. These serial port parameters must be set so they match the serial port parameters on - Страница 40 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.1.2 Console Server Mode Select Console Server Mode to enable remote management access to the serial console that is attached to the serial port: Logging Level This specifies the level of information to be logged and monitored (refer to Chapter - Страница 41 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration Note: In Console Server mode, Users and Administrators can use SDT Connector to set up secure Telnet connections that are SSH tunneled from their client computers to the serial port on the Console Server with a simple point-and-click. To use SDT - Страница 42 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration SSH It is recommended that the User or Administrator uses SSH as the protocol for connecting to serial consoles attached to the Console Server when communicating over the Internet or any other public network. This will provide an authenticated, - Страница 43 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration Unauthenticated Telnet Selecting Unauthenticated Telnet enables Telnet access to the serial port without requiring the user to provide credentials. When a user accesses the Console Server to Telnet to a serial port they are normally given a - Страница 44 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration Single Connection 4.1.3 This setting limits the port to a single connection so if multiple users have access privileges for a particular port only one user at a time can be accessing that port (i.e. port “snooping” is not permitted) SDT Mode - Страница 45 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.1.6 Serial Bridging Mode With serial bridging, the serial data on a nominated serial port on one Console Server is encapsulated into network packets and then transported over a network to a second Console Server where is then represented as - Страница 46 из 274
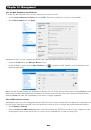
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.2 Add/ Edit Users The Administrator uses this menu selection to set up, edit and delete users and to define the access permissions for each of these users. Users can be authorized to access specified Console Server serial ports and specified - Страница 47 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration To set up new Groups and new users, and to classify users as members of particular Groups: • Select Serial & Network: Users & Groups to display the configured Groups and Users • Click Add Group to add a new Group • Add a Group name and - Страница 48 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.3 Authentication Refer to Chapter 9.1 - Remote Authentication Configuration for authentication configuration details 4.4 Network Hosts To access a locally networked computer or device (referred to as a Host) you must identify the Host and - Страница 49 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.5 Trusted Networks The Trusted Networks facility gives you an option to nominate specific IP addresses that users (Administrators and Users) must be located at, to have access to Console Server serial ports: • Select Serial & Network: Trusted - Страница 50 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.6 Serial Port Cascading Cascaded Ports enables you to cluster distributed Console Servers so that a large number of serial ports (up to 1000) can be configured and accessed through one IP address and managed through the one Management Console. - Страница 51 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.6.2 Manually generate and upload SSH keys Alternately if you have a RSA or DSA key pair you can manually upload them to the Master and Slave Console Servers. Note: If you do not already have RSA or DSA key pair and you do not wish to use you - Страница 52 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.6.3 Configure the slaves and their serial ports You can now begin setting up the Slaves and configuring Slave serial ports from the Master Console Server: • Select Serial & Network: Cascaded Ports on the Master’s Management Console: • To add - Страница 53 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.7 Serial Port Redirection Tripp Lite’s VirtualPort software delivers the virtual serial port technology your Windows applications need to open remote serial ports and read the data from serial devices that are connected to your Console Server. - Страница 54 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.7.2 Configure the VirtualPort client Creating the VirtualPort client connection will initiate a virtual serial port data redirection to the remote Console Server using TCP/IP protocol • Click on Add Ports • Specify a name to identify this - Страница 55 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration • To configure a COM port you have created simply click on the desired COMx label in the left hand menu tree • In the Properties window you can edit the IP Address or TCP Port to be used to connect to that COM port • You can then configure the - Страница 56 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration • Check Receive DSR/DCD/CTS changes if the flow control signal status from the physical serial port on Console Server is to be reflected back to the Windows COM port driver (as some serial communications applications prefer to run without any - Страница 57 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.8 Managed Devices Managed Devices presents a consolidated view of all the connections to a device that can be accessed and monitored through the Console Server. To view the connections to the devices: • Select Serial&Network: Managed Devices - Страница 58 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration To add a new serially connected Managed Device: • Configure the serial port using the Serial&Network: Serial Port menu (refer Section 4.1 -Configure Serial Port) • Select Serial&Network: Managed Devices and click Add Device • Enter a Device Name - Страница 59 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration • Select the Authentication Method to be used, either RSA digital signatures or a Shared secret (PSK) o If you select RSA you will asked to click here to generate keys. This will generate an RSA public key for the console server (the Left Public - Страница 60 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration • In Right Address enter the public IP or DNS address of the remote end of the tunnel (only if the remote end has a static or dyndns address). Otherwise leave this blank • If the VPN gateway is serving as a VPN gateway to a local subnet (e.g. - Страница 61 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.10.1 Enable the OpenVPN • Select OpenVPN on the Serial & Networks menu • Click Add and complete the Add OpenVPN Tunnel screen • Enter any descriptive name you wish to identify the OpenVPN Tunnel you are adding, for example NorthStOutlet-VPN • - Страница 62 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.10.2 Configure as Server or Client • Complete the Client Details or Server Details depending on the Tunnel Mode selected. o If Client has been selected, the Primary Server Address will be the address of the OpenVPN Server. o If Server has been - Страница 63 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration • To enable OpenVPN, Edit the OpenVPN tunnel • Check the Enabled button. • Apply to save changes Note: Please make sure that the console server system time is correct when working with OpenVPN. Otherwise authentication issues may arise • Select - Страница 64 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.10.3 Windows OpenVPN Client and Server set up Windows does not come with an OpenVPN server or client. This section outlines the installation and configuration of a Windows OpenVPN client or a Windows OpenVPN server and setting up a VPN - Страница 65 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration The Windows client/server configuration file options are: Options Description #description: This is a comment describing the configuration. Comment lines start with a ‘#’ and are ignored by OpenVPN. Client server Specify whether this will be a - Страница 66 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration To initiate the OpenVPN tunnel following the creation of the client/server configuration files: • Right click on the OpenVPN icon in the Notification Area • Select the newly created client or server configuration. For example, BL_client • Click - Страница 67 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.11 PPTP VPN Console Servers with Firmware V3.5.2 and later, include a PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) server. PPTP is typically used for communications over a physical or virtual serial link. The PPP endpoints define a virtual IP - Страница 68 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.11.1 Enable the PPTP VPN server • Select PPTP VPN on the Serial & Networks menu • Select the Enable check box to enable the PPTP Server • Select the Minimum Authentication Required. Access is denied to remote users attempting to connect using - Страница 69 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.11.2 Add a PPTP user • Select Users & Groups on the Serial & Networks menu and complete the fields as covered in section 4.2. • Ensure the pptpd Group has been checked, to allow access to the PPTP VPN server. Note - users in this group will - Страница 70 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.11.3 Set up a remote PPTP client Ensure the remote VPN client PC has Internet connectivity. To create a VPN connection across the Internet, you must set up two networking connections. One connection is for the ISP, and the other connection is - Страница 71 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.12 IP Passthrough IP Passthrough is used to make a modem connection (e.g. the Appliance’s internal cellular modem) appear like a regular Ethernet connection to a third-party downstream router, allowing the downstream router to use the - Страница 72 из 274
Chapter 4: Serial Port, Device and User Configuration 4.12.3 IP Passthrough configuration To configure IP Passthrough: • Click Serial & Network: IP Passthrough and check Enable • Select the Appliance Modem to use for upstream connectivity • Optionally, enter the MAC Address of downstream router’s - Страница 73 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band The Console Server has a number of failover and out-of-band access capabilities to ensure availability in the event there are difficulties in accessing the Console Server through the principal network path. This chapter covers: • Out-of-band (OoB) - Страница 74 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.1.1 Configure dial-in PPP To enable dial-in PPP access on the Console Server modem port/ internal modem: • Select the System: Dial menu option and the port to be configured (Serial DB9 Port or Internal Modem Port) Note: The Console Server’s - Страница 75 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band None PAP CHAP MSCHAPv2 • With this selection, no username or password authentication is required for dial-in access. This is not recommended. Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) is the usual method of user authentication used on the internet: sending - Страница 76 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band • Enter the PPP User Name and Password for have set up for the Console Server 5.1.4 Set up earlier Windows clients for dial-in • For Windows 2000, the PPP client set up procedure is the same as above, except you get to the Dial-Up Networking Folder by - Страница 77 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.2 OoB Broadband Access The B096-048/032/016 Console Server Management Switch has a second Ethernet network port that can be configured for alternate and OoB (out-of-band) broadband access. With two active broadband access paths to the Console Server, - Страница 78 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band • Specify the Probe Addresses of two sites (the Primary and Secondary) that the B096-048/032/016 is to ping to determine if Network (eth0) is still operational • Then configure Management LAN Interface (eth1) with the same IP setting that you used for - Страница 79 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.4.2 Dial-Out Failover The Console Servers can also be configured for dial-out failover— so a dial-out PPP connection is automatically set up in the event of a disruption in the principal management network: • When configuring the principal network - Страница 80 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.5 Firewall & Forwarding Console Servers provide basic firewalled routing, NAT (Network Address Translation), packet filtering and port forwarding support on all network interfaces. 5.5.1 Configuring network forwarding and IP masquerading To use a - Страница 81 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band • Find the Source Network to be routed, and then tick the relevant Destination Network to enable Forwarding For example to configure a dual Ethernet device such as a B096-048, B096-032 or B096-016 Console Server Management Switch: • The Source Network - Страница 82 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.5.2 Configuring client devices Client devices on the local network must be configured with Gateway and DNS settings. This can be done statically on each device, or using DHCP Manual Configuration: Manually set a static gateway address (being the - Страница 83 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.5.3 Port/Protocol Forwarding When using IP Masquerading, devices on the external network cannot initiate connections to devices on the internal network. To work around this, Port Forwards can be set up to allow external users to connect to a specific - Страница 84 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.5.4 Firewall Rules Firewall rules can be used to block or allow traffic through an interface based on port number, direction (ingress or egress) and protocol. This can be used to allow custom on box services, or block traffic based on policy. To setup - Страница 85 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band The firewall rules are processed in a set order- from top to bottom. So rule placement is important. For example with the following rules, all traffic coming in over the Network Interface is blocked except when it comes from two nominated IP addresses - Страница 86 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band Note: Your 4G LTE carrier may have provided you with details for configuring the connection, including APN (Access Point Name), PIN code (optional PIN code that may be required to unlock the SIM card), Username/Password, etc. In most cases, you will - Страница 87 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band • You can measure the received signal strength from the Cellular Statistics page on the Status: Statistics screen. This will display the current state of the cellular modem, including the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) Note: Received Signal - Страница 88 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.7 Cellular Operation When set up as a console server, the cellular modem can be set up to connect to the carrier in one of three modes: • Cellular router mode – In this case, the dial-out connection to the carrier’s cellular network is always on and - Страница 89 из 274
Chapter 5: Firewall, Failover and Out-of-Band 5.7.2 Cellular failover setup In this mode, a dial-out cellular connection is established only when the main network is disrupted. The cellular connection will remain idle in a low power state and will only be activated in the event of a ping failure. - Страница 90 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector Each Console Server has an embedded SSH server and uses SSH tunneling. This enables one Console Server to securely manage all the systems and network devices in the data center, using text-based console tools (such as SSH, Telnet, SoL) or graphical - Страница 91 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.1 Configuring for SDT Tunneling to Hosts To set up the Console Server to SDT access a network attached host, the host and the permitted services that are to be used in accessing that host need to be configured on the gateway, and User access - Страница 92 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.2 SDT Connector Configuration The SDT Connector client works with all Console Servers. Each of these remote Console Servers has an embedded OpenSSH based server. This server can be configured to port forward connections from the SDT Connector client - Страница 93 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.2.2 Configuring a new gateway in the SDT Connector client To create a secure SSH tunnel to a new Console Server: icon or select the File: New Gateway menu option • Click the New Gateway • Enter the IP or DNS Address of the Console Server and the SSH - Страница 94 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.2.3 Auto-configure SDT Connector client with the user’s access privileges Each user on the Console Server has an access profile. This has been configured with the specific connected hosts and serial port devices the user has authority to access, and - Страница 95 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.2.4 • Make an SDT connection through the gateway to a host Simply point at the host to be accessed and click on the service to be used in accessing that host. The SSH tunnel to the gateway is then automatically established, the appropriate ports - Страница 96 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.2.5 Manually adding hosts to the SDT Connector gateway For each gateway, you can manually specify the network connected hosts that will be accessed through that Console Server; and for each host, specify the services that will used in communicating - Страница 97 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.2.6 Manually adding new services to the new hosts To extend the range of services that can be used when accessing hosts with SDT Connector: • Select Edit: Preferences and click the Services tab. Click Add • Enter a Service Name and click Add • Under - Страница 98 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector • On the Add Service screen, you can click Add as many times as needed to add multiple new port redirections and associated clients You may also specify Advanced port redirection options: • Enter the local address to bind to when creating the local - Страница 99 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.2.7 Adding a client program to be started for the new service Clients are local applications that may be launched when a related service is clicked. To add to the pool of client programs: • Select Edit: Preferences and click the Client tab. Click - Страница 100 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector Also some clients are launched in a command line or terminal window. The Telnet client is an example of this: • Click OK 6.2.8 Dial-in configuration If the client computer is dialing into Local/Console port on the Console Server, you will need to set - Страница 101 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.3 SDT Connector to Management Console SDT Connector can also be configured for browser access to the gateway’s Management Console – and for Telnet or SSH access to the gateway command line. For these connections to the gateway itself, you must - Страница 102 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.4 SDT Connector - Telnet or SSH Serial Device Connection SDT Connector can also be used to access text consoles on devices that are attached to the Console Server’s serial ports. For these connections, you must configure the SDT Connector client - Страница 103 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.5 SDT Connector OoB Connection SDT Connector can also be set up to connect to the Console Server via out-of-band (OoB). OoB access uses an alternate path for connecting to the Console Server (i.e. not the one used for regular data traffic). OoB - Страница 104 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector To make the OoB connection using SDT Connector: • Select the gateway and click Out Of Band. The status bar will change color to indicate this gateway is now being access using the OoB link rather than the primary link When you connect to a service on - Страница 105 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.7 SDT Connector Public Key Authentication SDT Connector can authenticate against an SSH gateway using your SSH key pair rather than requiring your to enter your password. This is known as public key authentication. To use public key authentication - Страница 106 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.8 Setting up SDT for Remote Desktop Access Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) enables the system manager securely to access and manage remote Windows computers: to reconfigure applications and user profiles, upgrade the server’s operating - Страница 107 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector • To set the user(s) who can remotely access the system with RDP, click Add on the Remote Desktop Users dialog box Note: If you need to set up new users for Remote Desktop access, open User Accounts in the Control Panel and proceed through the steps - Страница 108 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector • Click Connect Note: The Remote Desktop Connection software is pre-installed on Windows XP. However, for earlier Windows computers, you will need to download the RDP client: • Go to the Microsoft Download Center site - Страница 109 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector Note: The rdesktop client is supplied with Red Hat 9.0: • rpm -ivh rdesktop-1.2.0-1.i386.rpm For Red Hat 8.0 or other distributions of Linux; download source, untar, configure, make, make then install. rdesktop currently runs on most UNIX based - Страница 110 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.9 SDT SSH Tunnel for VNC Alternately, with SDT and Virtual Network Computing (VNC), Users and Administrators can securely access and control Windows 98/NT/2000/XP/2003, Linux, Macintosh, Solaris and UNIX computers. There’s a range of popular VNC - Страница 111 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector • To set up a persistent VNC server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4: o o o o o Set a password using vncpasswd Edit /etc/sysconfig/vncservers Enable the service with chkconfig vncserver on Start the service with service vncserver start Edit - Страница 112 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector • You can then establish the VNC connection by simply activating the VNC Viewer software on the Viewer computer and entering the password Note: For general background reading on Remote Desktop and VNC access, we recommend the following: • • • • • • • - Страница 113 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.10 SDT IP Connection to Hosts Network (IP) protocols like RDP, VNC and HTTP can also be used to connect to host devices that are serially connected through their COM port to the Console Server. To do this you must: • establish a PPP connection - Страница 114 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector • Specify which Users will be allowed to use this connection. This should be the same Users who were given Remote Desktop access privileges in the earlier step. Click Next • On the Network Connection screen, select TCP/IP and click Properties • Select - Страница 115 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector Note: You can choose any TCP/IP addresses as long as they are addresses which are not used anywhere else on your network. The From: address will be assigned to the Windows XP/2003 computer and the To: address will be used by the Console Server. For - Страница 116 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.10.2 Set up SDT Serial Ports on Console Server To set up RDP (and VNC) forwarding on the Console Server’s Serial Port that is connected to the Windows computer COM port: • Select the Serial & Network: Serial Port menu option and click Edit (for the - Страница 117 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector 6.11 SSH Tunneling using other SSH clients (e.g. PuTTY) As covered in the previous sections of this chapter we recommend you use the SDT Connector client software that is supplied with the Console Server. However there’s also a wide selection of - Страница 118 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector o If your destination computer is serially connected to the Console Server, set the Destination as <port label>:3389 e.g. if the Label you specified on the serial port on the Console Server is win2k3, then specify the remote host as win2k3:3389 . - Страница 119 из 274
Chapter 6: Secure SSH Tunneling & SDT Connector o If you are connecting as a User in the “users” group then you can only SSH tunnel to Hosts and Serial Ports where you have specific access permissions o If you are connecting as an Administrator (in the “admin” group) then you can connect to any - Страница 120 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging This chapter describes the automated response, alert generation and logging features of the Console Server. The new Auto-Response facility (in firmware V3.5.1 and later) extends on the basic Alert facility available in earlier firmware revisions. - Страница 121 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging • Check Disable Auto-Response at specific times and you will be able to periodically disable Auto-Responses between specified times of day To configure the condition that will trigger the Auto-Response: • Click on the Check Condition type (e.g. - Страница 122 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging Note: Before configuring Environmental Checks as the trigger in Auto-Response you will need first to configure the Temp and/ or Humidity sensors on your attached EMD 7.1.2 Alarms and Digital Inputs To set the status of any attached Smoke or Water - Страница 123 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.1.5 Serial Login/Logout To monitor serial ports and check for login/logout or pattern matches for Auto-Response triggers events: • Click on Serial Login/Logout as the Check Condition. Then in the Serial Login/Logout Check menu select Trigger on - Страница 124 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.1.8 Custom Check This check allows users to run a nominated custom script with nominated arguments whose return value is used as an Auto-Response trigger event: • Click on Custom Check as the Check Condition • Create an executable trigger check - Страница 125 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.1.10 Log In/Out Check To configure Web Log In/Out as the trigger event: • Click on the Web UI Authentication as the Check Condition • Check Trigger on Login (Logout) to trigger when a user logs into (or out of) the Web UI • Check Trigger on - Страница 126 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.1.12 Routed data usage check This check monitors the specified input interface for data usage that is being routed through the appliance and out another interface such as the Internal Cellular Modem. It is particularly useful in IP Passthrough - Страница 127 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.2 Trigger and Resolve Actions To configure the sequence of actions taken in the event of the trigger condition: • For a nominated Auto-Response - with a defined Check Condition - click on Add Trigger Action (e.g. Send Email or Run Custom Script) - Страница 128 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.2.4 Run Custom Script on Trigger • Click on Run Custom Script as the Add Trigger Action. Enter a unique Action Name and set the Action Delay Time • Create a script file to execute when this action is triggered and enter the Script Executable file - Страница 129 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.2.8 Resolve Actions Actions can also be scheduled to be taken when a trigger condition has been resolved: • For a nominated Auto-Response - with a defined trigger Check Condition - click on Add Resolve Action (e.g. Send Email or Run Custom Script) - Страница 130 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging SMS via Email Gateway To use SMTP SMS, the Administrator must configure a valid SMTP server for sending the email: • In the SMTP Settings field in the Alerts & Logging: SMTP & SMS menu select SMS Gateway. An SMS via Email Gateway field will appear • - Страница 131 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging • Configure SNMP v3 if required. For SNMP v3 messages, the user’s details and security level must match what the receiving SNMP Network Manager is expecting. SNMP v3 mandates that the message will be rejected unless the SNMPv3 user sending the trap - Страница 132 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.3 Remote Log Storage Before activating Serial or Network Port Logging on any port or UPS logging, you must specify where those logs are to be saved: • Select the Alerts & Logging: Port Log menu option and specify the Server Type to be used, and - Страница 133 из 274
Chapter 7: Alerts, Automated Response and Logging 7.5 Network TCP or UDP Port Logging The Console Servers can also log any access to and communications with network attached Hosts. • For each Host, when you set up the Permitted Services which are authorized to be used, you also must set up the - Страница 134 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment The B094-008-2E-M-F, B094-008-2E-V, B095-004/003 and B092-016 Console Servers and B096-048/032/016 Console Server Management Switch products embed software that can be used to manage connected Power Distribution Systems (PDU’s), IPMI devices and Uninterruptible - Страница 135 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment Now you have set up a new serially or network connected RPC device, this will automatically create a corresponding new Managed Device with the same Name /Description as the RPC The outlet names on the RPC/PDU Managed Device will by default be “Outlet 1” “Outlet 2”. - Страница 136 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment 8.1.2 RPC alerts You can now set PDU and IPMI alerts using Alerts & Logging: Alerts (refer to Chapter 7) 8.1.3 RPC status You can monitor the current status of your network and serially connected PDU’s and IPMI RPC’s • Select the Status: RPC Status menu. A table - Страница 137 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment 8.1.4 User power management The Power Manager enables both Users and Administrators to access and control the configured serial and network attached PDU power strips, and servers with embedded IPMI service processors or BMC’s: • Select the Manage: Power and the - Страница 138 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment 8.2 Uninterruptible Power Supply Control (UPS) The Console Servers manage UPS hardware using Network UPS Tools (refer Section 8.2.6 for an overview of embedded open source Network UPS Tools - NUT software) 8.2.1 Managed UPS connections A Managed UPS is a UPS that is - Страница 139 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment • Select the Serial & Network: UPS Connections menu. The Managed UPSes section will display all the UPS connections that have already been configured. • Click Add UPS • Enter a UPS Name and Description (optional) and identify if the UPS will be Connected Via USB or - Страница 140 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment • Select the Driver that will be used to communicate with the UPS. The drop-down menu presents a full selection of drivers from the latest Network UPS Tools (NUT version 2.2.0) and additional information on compatible UPS hardware can be found at - Страница 141 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment 8.2.3 Configuring powered computers to monitor a Managed UPS Once you have added a Managed UPS, each server that is drawing power through the UPS should be setup to monitor the UPS status as a Slave. This is done by installing the NUT package on each server, and - Страница 142 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment 8.2.4 UPS alerts You can now set UPS alerts using Alerts & Logging: Alerts (refer to Chapter 7) 8.2.5 UPS status You can monitor the current status of all your Managed or Monitored UPS’s, whether they are on the network or connected serially or via USB: • Select the - Страница 143 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment 8.2.6 Overview of Network UPS Tools (NUT) Network UPS Tools (NUT) is a group of open source programs that provide a common interface for monitoring and administering UPS hardware; and ensuring safe shutdowns of the systems which are connected. NUT can be configured - Страница 144 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment 8.3 Environmental Monitoring The Environmental Monitoring Device (EMD), model B090-EMD, can be connected to any Console Server serial port and each Console Server can support multiple EMD’s. Each EMD has one temperature and one humidity sensor and one general - Страница 145 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment 8.3.1 Connecting the EMD The Environmental Monitoring Sensor (EMD) connects to any serial port on the Console Server via a special EMD Adapter and standard CAT5 cable. The EMD is powered over this serial connection and communicates using a custom handshake protocol. - Страница 146 из 274
Chapter 8: Power and Environment • Enter a Name and Description for the EMD and select pre-configured serial port that the EMD will be Connected Via • Provide Labels for each of the two alarms • Check Log Status and specify the Log Rate (minutes between samples) if you wish the status from this EMD - Страница 147 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication The Tripp Lite Console Server is a dedicated Linux computer, and it embodies popular and proven Linux software modules for secure network access (OpenSSH) and communications (OpenSSL) and sophisticated user authentication (PAM, RADIUS, TACACS+, Kerberos and LDAP). • This - Страница 148 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication 9.1.2 TACACS authentication Perform the following procedure to configure the TACACS+ authentication method to be used whenever the Console Server or any of its serial ports or hosts is accessed: • Select Serial and Network: Authentication and check TACAS or LocalTACACS or - Страница 149 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication 9.1.3 RADIUS authentication Perform the following procedure to configure the RADIUS authentication method to be used whenever the Console Server or any of its serial ports or hosts is accessed: • Select Serial and Network: Authentication and check RADIUS or LocalRADIUS or - Страница 150 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication 9.1.4 LDAP authentication With firmware version 3.11 and later, LDAP authentication now supports OpenLDAP servers using the Posix-style schema for user and group definitions. Performing simple authentication against any LDAP server (AD or OpenLDAP) follow the common LDAP - Страница 151 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication Perform the following procedure to configure the LDAP authentication method to be used whenever the Console Server or any of its serial ports or hosts is accessed: • Select Serial and Network: Authentication and check LDAP or LocalLDAP or LDAPLocal or LDAPDownLocal • Enter - Страница 152 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication 9.1.5 RADIUS/TACACS user configuration Users may be added to the local Console Server appliance. If they are not added and they log in via remote AAA, a user will be added for them. This user will not show up in the configurators unless they are specifically added, at - Страница 153 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication attribute, in the following format: :group_name=testgroup1,users: The above example sets the remote user as a member of testgroup1 and users if groups with those names exist on the Console Server. Any groups which do not exist on the Console Server are ignored. When - Страница 154 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication 9.1.8 Remote groups with LDAP authentication Unlike RADIUS, LDAP has built in support for group provisioning, which makes setting up remote groups easier. The console server will retrieve a list of all the remote groups that the user is a direct member of, and compare - Страница 155 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication • Ensure the LDAP service is operational and group names are correct within the Active Directory 9.1.9 Idle timeout You can specify amount of time in minutes the console server waits before it terminates an idle ssh, pmshell or web connection. • Select Serial and Network: - Страница 156 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication 9.1.10 Kerberos authentication The Kerberos authentication can be used with UNIX and Windows (Active Directory) Kerberos servers. This form of authentication does not provide group information, so a local user with the same username must be created, and permissions set. - Страница 157 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication TACACS Example: user = tim { service = raccess { priv-lvl = 11 port1 = xxxxx/port02 port2 = 192.168.254.145/port05 } global = cleartext mit } RADIUS Example: paul Cleartext-Password := "luap" Service-Type = Framed-User, Fall-Through = No, - Страница 158 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication 9.4 SSL Certificate The Console Server uses the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol for encrypted network traffic between itself and a connected user. During the connection establishment the Console Server has to expose its identity to the user’s browser using a - Страница 159 из 274
Chapter 9: Authentication Common name This is the network name of the Console Server once it is installed in the network (usually the fully qualified domain name). It is identical to the name that is used to access the Console Server with a web browser (without the “http://” prefix). In case the - Страница 160 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration Nagios is a powerful, highly extensible open source tool for monitoring network hosts and services. The core Nagios software package will typically be installed on a server or virtual server, the central Nagios server. Tripp Lite Console Servers can operate in - Страница 161 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration 10.2 Central management and setting up SDT for Nagios The Nagios solution has three parts: the Central Nagios server, Distributed Console Servers and the SDT for Nagios software. Central Nagios server • A vanilla Nagios 2.x or 3.x installation (typically on a Linux - Страница 162 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration 10.2.2 Set up distributed Console Servers This section provides a brief walk-through on configuring a single Console Server to monitor the status of one attached network host (a Windows IIS server running HTTP and HTTPS services) and one serially attached device (the - Страница 163 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration • Scroll down to Nagios Settings and check Enable Nagios • Click New Check and select Check Ping. Click check-host-alive • Click New Check and select Check Permitted TCP. Select Port 3389 • Click New Check and select Check TCP. Select Port 80 • Click New Check and - Страница 164 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration 10.3 Configuring Nagios distributed monitoring To activate the Console Server’s Nagios distributed monitoring: • Nagios integration must be enabled and a path established to the central/upstream Nagios server • If the Console Server is to periodically report on - Страница 165 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration 10.3.2 Enable NRPE monitoring Enabling NRPE allows you to execute plug-ins (such as check_tcp and check_ping) on the remote Console Server to monitor serial or network attached remote servers. This will offload CPU load from the upstream Nagios monitoring machine - Страница 166 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration 10.3.3 Enable NSCA monitoring NSCA is the mechanism that allows you to send passive check results from the remote Console Server to the Nagios daemon running on the monitoring server. To enable NSCA: • Select System: Nagios and check NSCA Enabled • Select the - Страница 167 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration 10.3.4 Configure selected Serial Ports for Nagios monitoring The individual Serial Ports connected to the Console Server to be monitored must be configured for Nagios checks. Refer to Chapter 4.4: Network Host Configuration for details on enabling Nagios monitoring - Страница 168 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration • The Nagios Check nominated as the check-host-alive check is used to determine whether the network host itself is up or down • Typically this will be Check Ping – although in some cases the host will be configured not to respond to pings • If no check-host-alive - Страница 169 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration 10.4 Advanced Distributed Monitoring Configuration 10.4.1 Sample Nagios configuration An example configuration for Nagios is listed below. It shows how to set up a remote Console Server to monitor a single host, with both network and serial connections. Each check has - Страница 170 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration define service { service_description serial-signals-server host_name server use generic-service check_command check_serial_status active_checks_enabled 0 passive_checks_enabled 1 } define servicedependency{ name tripplite_nrpe_daemon_dep host_name tripplite - Страница 171 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration define service { service_description Host Ping host_name server use generic-service check_command check_ping_via_tripplite } define service { service_description host-ping-server host_name server use generic-service check_command check_ping_via_tripplite - Страница 172 из 274
Chapter 10: Nagios Integration 10.4.2 Basic Nagios plug-ins Plug-ins are compiled executables or scripts that can be scheduled to be run on the Console Server to check the status of a connected host or service. This status is then communicated to the upstream Nagios server which uses the results to - Страница 173 из 274
Chapter 11: System Management This chapter describes how the Administrator can perform a range of general system administration and configuration tasks on the Console Server, such as: • Applying Soft and Hard Resets to the gateway • Re-flashing the firmware • Configuring the Date, Time and NTP • - Страница 174 из 274
Chapter 11: System Management 11.2 Upgrade Firmware Before upgrading you should ascertain if you are already running the most current firmware in your gateway. Your Console Server will not allow you to upgrade to the same or an earlier version. • The Firmware version is displayed in the header of - Страница 175 из 274
Chapter 11: System Management 11.3 Configure Date and Time It is recommended that you set the local Date and Time in the Console Server as soon as it is configured. Features such as Syslog and NFS logging use the system time for time-stamping log entries, while certificate generation depends on a - Страница 176 из 274
Chapter 11: System Management 11.4 Configuration Backup It is recommended that you back up the Console Server configuration whenever you make significant changes (such as adding new Users or Managed Devices) or before performing a firmware upgrade. • Select the System: Configuration Backup menu - Страница 177 из 274
Chapter 11: System Management After saving a local configuration backup, you may choose to use it as the alternate default configuration. When the Console Server is reset to factory defaults, it will then load your alternate default configuration instead of its factory settings: • To set an - Страница 178 из 274
Chapter 11: System Management • Click Apply to run all the configurators in the queue • Alternately click Cancel and this will discard all the delayd configuration changes Note: All the queued configuration changes will be lost if Cancel is selected To disable the Delayed Configuration Commits - Страница 179 из 274
Chapter 12: Status Reports This chapter describes the dashboard feature and the status reports that are available: • Port Access and Active Users • Statistics • Support Reports • Syslog • Dashboard The UPS, RPC and Environmental Status reports are covered in Chapter 8 12.1 Port Access and Active - Страница 180 из 274
Chapter 12: Status Reports 12.2 Statistics The Statistics report provides a snapshot of the status, current traffic and other activities and operations of your Console Server: • Select the Status: Statistics 12.3 Support Reports The Support Report provides useful status information that will assist - Страница 181 из 274
Chapter 12: Status Reports 12.4 Syslog The Linux System Logger in the Console Server maintains a record of all system messages and errors: • Select Status: Syslog The syslog record can be redirected to a remote Syslog Server: • Enter the remote Syslog Server Address and Syslog Server Port details - Страница 182 из 274
Chapter 12: Status Reports 12.5.1 Configuring the Dashboard Only users who are members of the admin group (and the root user) can configure and access the dashboard. To configure a custom dashboard: • Select System: Configure Dashboard and select the user (or group) you are configuring this custom - Страница 183 из 274
Chapter 12: Status Reports To configure what is to be displayed by each widget: • Go to the Configure Widgets panel and configure each selected widget (e.g. specify which UPS status is to be displayed on the ups widget or the maximum number of Managed Devices to be displayed in the devices widget • - Страница 184 из 274
Chapter 13: Management The Console Server has a small number of Manage reports and tools that are available to both Administrators and Users: • Access and control authorized devices • View serial port logs and host logs for those devices • Use SDT Connector or the Web Terminal to access serially - Страница 185 из 274
Chapter 13: Management 13.2 Port and Host Log Management Administrators and Users can view logs of data transfers to connected devices. • Select Manage: Port Logs and the serial Port # to be displayed • To display Host logs select Manage: Host Logs and the Host to be displayed 13.3 Terminal - Страница 186 из 274
Chapter 13: Management 13.3.1.2 Web Terminal to Serial Device To enable the Web Terminal service for each serial port you want to access: • Select Serial & Network: Serial Port and click Edit. Ensure the serial port is in Console Server Mode • Check Web Terminal and click Apply Administrator and - Страница 187 из 274
Chapter 13: Management Note: SDT Connector must be installed on the computer you are browsing from and the Console Server must be added as a gateway - as detailed in Chapter 6 13.4 Power Management Administrators and Users can access and manage the connected power devices. • Select Manage: Power - Страница 188 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration For those who prefer to configure their Console Server at the Linux command line level (rather than use a browser and the Management Console), this chapter describes using command line access and the config tool to manage the Console Server and configure the - Страница 189 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration The config tool Syntax config [ -ahv ] [ -d id ] [ -g id ] [ -p path ] [ -r configurator ] [ -s id=value ] [ -P id ] Description The config tool is designed to perform multiple actions from one command if need be, so if necessary options can be chained - Страница 190 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration The registered configurators are: alerts auth cascade console dhcp dialin eventlog hosts ipaccess ipconfig nagios power serialconfig services slave systemsettings time ups users There are three ways to delete a config element value. The simplest way is use the - Страница 191 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration The following command will synchronize the live system with the new configuration: # config -r serialconfig Note: Supported serial port baud-rates are ‘50’, ‘75’, ‘110’, ‘134’, ‘150’, ‘200’, ‘300’, ‘600’, ‘1200’, ‘1800’, ‘2400’, ‘4800’, ‘9600’, '19200', - Страница 192 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration SDT mode To enable access over SSH to a host connected to serial port 5: # config -s config.ports.port5.mode=sdt # config -s config.ports.port5.sdt.ssh=on To configure a username and password when accessing this port with Username = user1 and Password = - Страница 193 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.2 Adding and removing Users Firstly, determine the total number of existing Users (if you have no existing Users you can assume this is 0): # config -g config.users.total This command should display config.users.total 1. Note that if you see - Страница 194 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.3 Adding and removing User Groups The Console Server is configured with a few default user groups (even though only two of these groups are visible in the Management Console GUI). To find out how many groups are already present: # config -g - Страница 195 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.4 Authentication To change the type of authentication for the Console Server: # config -s config.auth.type='authtype' 'authtype' can be: Local LocalTACACS TACACS TACACSLocal TACACSDownLocal LocalRADIUS RADIUS RADIUSLocal RADIUSDownLocal LocalLDAP LDAP - Страница 196 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.5 Network Hosts To determine the total number of currently configured hosts: # config -g config.sdt.hosts.total Assume this value is equal to 3. If you add another host, make sure to increment the total number of hosts from 3 to 4: # config -s - Страница 197 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration Assuming we already have one managed device, our new device will be device 2. Issue the following commands: # # # # # config config config config config -s -s -s -s -s config. devices.device2.connections.connection1.name=192.168.3.10 config. - Страница 198 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.8 UPS Connections Managed UPS Systems Before adding a managed UPS, make sure that at least 1 port has been configured to run in 'device mode', and that the device is set to 'ups'. To add a managed UPS with the following values: Connected via Port 1 UPS - Страница 199 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration Remote UPSes To add a remote UPS with the following details (assuming this is our first remote UPS): UPS name oldUPS Description UPS in room 2 Address 192.168.50.50 Log status Disabled Log rate 240 seconds Run shutdown script Enabled # # # # # # # config - Страница 200 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.10 Environmental To configure an environmental monitor with the following details: Monitor name Monitor Description Temperature offset Humidity offset Enable alarm 1 ? Alarm 1 label Enable alarm 2 ? Alarm 2 label Logging enabled ? Log interval # # # # # # - Страница 201 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.12 Port log To configure serial/network port logging: # config -s config.eventlog.server.address='remote server ip address' # config -s config.eventlog.server.logfacility='facility' 'facility' can be: Daemon Local 0-7 Authentication Kernel User Syslog - Страница 202 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.13 Alerts You can add an email, SNMP or NAGIOS alert by following the steps below. The general settings for all alerts Assume this is our second alert, and we want to send alert emails to john@company.com and sms's to peter@compnany. com: # config -s - Страница 203 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration Environmental and Power Sensor Alert # config -s config.alerts.alert2.enviro.high.critical='critical value' # config -s config.alerts.alert2.enviro.high.warning='warning value' # config -s config.alerts.alert2.enviro.hysteresis='value' # config -s - Страница 204 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration Alarm Sensor Alert To set an alert for 'doorAlarm' and 'windowAlarm' which are two alarms connected to an environmental sensor called 'SensorInRoom3'. Both alarms are disabled on Mondays from 8:15am to 2:30pm: # # # # # # # # # # config config config config - Страница 205 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.15 SNMP To set-up the SNMP agent on the device: # # # # # # # # config config config config config config config config -s -s -s -s -s -s -s -s config.system.snmp.protocol=[ UDP | TCP ] config.system.snmp.trapport='port number' (default is 162) - Страница 206 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration Note: Not all devices have a management LAN interface. To configure a failover device in case of an outage: # config -s config.interfaces.wan.failover.address1='ip address' # config -s config.interfaces.wan.failover.address2='ip address' # config -s - Страница 207 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration # # # # # # # config config config config config config config -s -s -s -s -s -s -s config.console.flow=Hardware config.console.initstring=ATQ0V1H0 config.console.ppp.enabled=on config.console.ppp.callback.enabled=on - Страница 208 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration 14.1.21 Services You can manually enable or disable network servers from the command line. For example if you wanted to guarantee the following server configuration: HTTP Server Enabled HTTPS Server Disabled Telnet Server Disabled SSH Server Enabled SNMP - Страница 209 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration To configure NSCA with the following settings: NSCA encryption NSCA password NSCA check-in interval NSCA port user to run as group to run as # # # # # # # config config config config config config config -s -s -s -s -s -s -s BLOWFISH (can be: [ None | XOR | - Страница 210 из 274
Chapter 14: Command Line Configuration Supported commands that have config files that can be altered include: portmanager inetd init ssh/sshd/scp/sshkeygen ucd-snmpd samba fnord (web server) sslwrap Commands you can run from the command line on the Console Server include:: loopback bash (shell) - Страница 211 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration Console Servers run the embedded Linux operating system. So Administrator class users can configure the Console Server and monitor and manage attached serial console and host devices from the command line using Linux commands and the config utility (as described - Страница 212 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.1.2 Running custom scripts when alerts are triggered Whenever an alert gets triggered, specific scripts get called. These scripts all reside in /etc/scripts/. Below is a list of the default scripts that get run for each applicable alert: • For a connection - Страница 213 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.1.3 Example script - Power cycling on pattern match If for example we had an RPC (PDU) connected to port 1 on a Console Server and also have some telecommunications device connected to port 2 and which is powered by the RPC outlet 3. Now assume the telecom - Страница 214 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.1.5 Deleting configuration values from the CLI The delete-node script is provided to help with deleting nodes from the command line. The "delete-node" script takes one argument, the node name you want to delete (e.g. "config.users.user1" or - Страница 215 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration TOTAL=`config -g $TOTALNODE | sed 's/.* //'` NEWTOTAL=$[ $TOTAL -1 ] # Make backup copy of config file cp /etc/config/config.xml /etc/config/config.bak echo "backup of /etc/config/config.xml saved in /etc/config/config.bak" if [ -z $NUMBER ] # test whether a - Страница 216 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration elif [ $NUMBER -lt $TOTAL ] # more than one item exists then # Modify the users list so user numbers are sequential # by shifting the users into the gap one at a time... echo "Deleting $1" LASTFIELDTEXT=`echo $LASTFIELD | sed 's/[0-9]//g'` CHECKTOTAL=`config -g - Страница 217 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.1.6 Power cycle any device upon a ping request failure The ping-detect script is designed to run specified commands when a monitored host stops responding to ping requests. The first parameter taken by the ping-detect script is the hostname/ IP address of the - Страница 218 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration if [ "$COUNTER" -eq 5 ] then COUNTER=0 "$@" sleep 2s fi done 15.1.7 Running custom scripts when a configurator is invoked A configurator is responsible for reading the values in /etc/config/config.xml and making the appropriate changes live. Some changes made by - Страница 219 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration To check if the backup was saved correctly: # /etc/scripts/backup-usb list If this command does not display "* config-20May" then there was an error saving the configuration. The set-default command takes an input file as an argument and renames it to - Страница 220 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.2 Advanced Portmanager The portmanger program manages the Console Server serial ports. It routes network connection to serial ports, checks permissions, and monitors and logs all the data flowing to/from the ports. 15.2.1 Portmanager commands pmshell The - Страница 221 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration The pmshell help message is NOT updated with the extra control command keys that may be configured. For example, to configure the Ctrl+p command to open the power menu when using serial port 3, enter the following in the console server’s command shell: config -s - Страница 222 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration pmchat The pmchat command acts similar to the standard chat command, but all serial port access is directed via the portmanager. Example: To run a chat script via the portmanager: # pmchat -v -f /etc/config/scripts/port08.chat < /dev/port08 For more information on - Страница 223 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration # pmusers --disconnect -n 5 Disconnect all users from port 5 (BranchRouter01)? (y/n) y 2 sessions were disconnected # pmusers --disconnect -u robertw -u pchunt -n 4 -n 6 Disconnect users robertw, pchunt from ports 4, 6? (y/n) y 10 sessions were disconnected # - Страница 224 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration • Here is a more complex script which reads from configuration to display the port label if available and denies access to the root user: </etc/config/pmshell-start.sh> #!/bin/sh PORT="$1" USER="$2" LABEL=$(config -g config.ports.port$PORT.label | cut -f2- -d' ') - Страница 225 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.4 IP- Filtering The Console Server uses the iptables utility to provide a stateful firewall of LAN traffic. By default rules are automatically inserted to allow access to enabled services, and serial port access via enabled protocols. The commands which add - Страница 226 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.5.3 Enable SNMP service Note: For firmware versions 3.10.2 and above, a new SNMP status and trap MIBS were created to provide more and better structured SNMP status and traps from console servers. There is an option in the SNMP menu to Use Legacy Notifications - Страница 227 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration • Complete the Location and Contact fields. The Location field should describe the physical location of the Console Server and will be used in response to requests for the SNMPv2-MIB::sysLocation.0 of the device. The Contact field refers to the person responsible - Страница 228 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration • Using the snmpwalk and snmpget commands, the status information can be retrieved from any console server. For example: snmpwalk -Oa -v1 -M .:/usr/share/snmp/mibs -c public b095 STATUS-MIB::ogStatus snmpget -Oa -v1 -M .:/usr/share/snmp/mibs -c public b095 - Страница 229 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.5.4 /etc/config/snmpd.conf The net-snmpd is an extensible SNMP which includes built-in support for a wide range of MIB information modules, and can be extended using dynamically loaded modules, external scripts and commands. snmpd when enabled should run with a - Страница 230 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration To set the SNMP Manager v3 Auth. Protocol and password fields: config –set="config.system.snmp.authprotocol3=SHA" or config --set="config.system.snmp.authprotocol3=MD5" config --set="config.system.snmp.authpassword3=password 1" To set the SNMP Manager v3 Privacy - Страница 231 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.6.2 Generating Public Keys (Linux) To generate new SSH key pairs use the Linux ssh-keygen command. This will produce an RSA or DSA public/private key pair and you will be prompted for a path to store the two key files e.g. id_dsa.pub (the public key) and id_dsa - Страница 232 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.6.4 Installing SSH Public Key Authentication (Linux) Alternately the public key can be installed on the unit remotely from the linux host with the scp utility as follows. Assuming the user on the Management Console is called "fred"; the IP address of the - Страница 233 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration If the Console Server device selected to be the server will only have one client device, then the authorized_keys file is simply a copy of the public key for that device. If one or more devices will be clients of the server, then the authorized_keys file will - Страница 234 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration • Click on the Generate button • Follow the instruction to move the mouse over the blank area of the program in order to create random data used by PUTTYGEN to generate secure keys. Key generation will occur once PUTTYGEN has collected sufficient random data • - Страница 235 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration This fingerprint is related to the host key of the remote server. Fingerprints are stored in ~/.ssh/known_hosts. To receive the fingerprint from the remote server, log in to the client as the required user (usually root) and establish a connection to the remote - Страница 236 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration • Select SSH Tunnel when configuring the Serial Bridging Setting Next you will need to set up SSH keys for each end of the tunnel and upload these keys to the Server and Client console servers. Client Keys: The first step in setting up ssh tunnels is to generate - Страница 237 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration It is advisable to create a new directory to store your generated keys. It is also possible to name the files after the device they will be used for. For example: $ mkdir keys $ ssh-keygen -t rsa Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save - Страница 238 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.7 Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Support Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a protocol developed by Netscape for transmitting private documents via the Internet. SSL works by using a private key to encrypt data that's transferred over the SSL connection. The Console - Страница 239 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.8.3 Installing the key and certificate The recommended method for copying files securely to the Console Server unit is with an SCP (Secure Copying Protocol) client. The scp utility is distributed with OpenSSH for most Unix distributions while Windows users can - Страница 240 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.9 Power Strip Control The Console Server supports a growing list of remote power-control devices (RPCs) which can be configured using the Management Console as described in Chapter 8. These RPCs are controlled using the open source NUT and PowerMan tools and - Страница 241 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration Some examples of powerman targets: Power on hosts bar,baz,foo01,foo02,...,foo05: powerman --on bar baz foo[01-05] Power on hosts bar,foo7,foo9,foo10: powerman --on bar,foo[7,9-10] Power on foo0,foo4,foo5: powerman --on foo[0,4-5] As a reminder to the reader, some - Страница 242 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration Here is a brief description of the elements of the XML entries in /etc/config/powerstrips.xml. <powerstrip> <id>Name or ID of the device support</id> <outlet port="port-id-1">Display Port 1 in menu</outlet> <outlet port="port-id-2">Display Port 2 in menu</outlet> - Страница 243 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.10 IPMItool The Console Server includes the ipmitool utility for managing and configuring devices that support the Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) version 1.5 and version 2.0 specifications. IPMI is an open standard for monitoring, logging, - Страница 244 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration -H <address> Remote server address can be an IP address or hostname. This option is required for lan and lanplus interfaces. -I <interface> Selects IPMI interface to use. Supported interfaces that are compiled in and visible in the usage help output. -L <privlvl> - Страница 245 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration COMMANDS help This can be used to get command-line help on ipmitool commands. It may also be placed at the end of commands to get option usage help. ipmitool help Commands: raw lan chassis event mc sdr sensor fru sel pef sol isol user channel session exec set Send - Страница 246 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration To run the CGI script on the Console Server: • Login to the B092-016 • Run: mount -o remount,rw /dev/hda1 / • Copy the script to /home/httpd/cgi-bin/ • Run: mount -o remount,ro /dev/hda1 / • Browse to: http://192.168.0.1/cgi-bin/yourscript.cgi where 192.168.0.1 is - Страница 247 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.14 Zero Touch Provisioning Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) was introduced with firmware release 3.15 to allow appliances to be provisioned during their initial boot from a DHCP server. 15.14.1 Preparation These are typical steps for configuration over a trusted - Страница 248 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration 15.14.4 How it works This section explains in detail how the Appliance uses DHCP to obtain its initial configuration. First, an appliance is either configured or unconfigured. ZTP needs it to be in an unconfigured state, which is only obtained in the following - Страница 249 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration • The system checks to see if it is still in an unconfigured state. If it is, then the network interface mode is set to DHCP. This effectively forces the system into a configured state, preventing a future reboot loop. • The system reboots Note: If all the URLs - Страница 250 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration B. Create the secure USB key 1. Format a USB flash drive as a single FAT32 volume. 2. Move the client.pem and ca-bundle.crt files onto the flash drive’s root directory. Configure lighttpd This is an example web server on Ubuntu 14.10. We will be putting the - Страница 251 из 274
Chapter 15: Advanced Configuration D. Set up the DHCP server This is on Ubuntu with the isc-dhcp-server package installed. We assume you have already set this up server DHCP leases. 1. Add this entry to /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf option space tripplite code width 1 length width 1; option - Страница 252 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client The B092-016 has a selection of management clients (Firefox browser, SSH, Telnet, VNC viewer, ICA, RDP) embedded as well as the Tripp Lite PowerAlert software. With these, the B092-016 provides rackside control of computers, networking, telecom, power and other managed - Страница 253 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client • The sixteen serial ports are pre-configured by default in Console Server mode for the B096-016 / B096-032 / B096-048 Console Server Management Switch or in UPS (PowerAlert) mode for the B092-016 Console Server with PowerAlert product. To change these settings, select - Страница 254 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client 16.1.2 Connect: Browser • Select Connect: Browser on the control panel and click on the Host/web site you have configured to be accessed using the browser. Sites can be internal or external. The B092-016 provides a powerful Mozilla Firefox browser with a licensed Sun Java - Страница 255 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client 16.1.3 Connect: VNC • Select Connect: VNC on the control panel and click on the VNC server Host to be accessed • The VNC Viewer client in your B092-016 will be started and a VNC connection window to the selected server will be opened • If the HostName was left blank when the - Страница 256 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client 16.1.4 Connect: SSH SSH is typically used to log into a remote machine and execute commands. • Select Connect: SSH on the control panel and click on the Host to be accessed • An SSH connection window will be opened. Enter the SSH login password and you will be securely - Страница 257 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client 16.1.5 Connect: IPMI The B092-016 control panel provides a number of IPMI tools for managing service processors or Baseboard Management Controllers (BMCs). These IPMI controls are built on the ipmitools program. Find more details on configuration options in http:// - Страница 258 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client 16.1.6 Connect: Remote Desktop (RDP) • Select Connect: RDP on the control panel and click on the Windows computer to be accessed • The rdesktop program in your B092-016 will be started, an RDP connection to the Remote Desktop server in the selected computer will be opened, - Страница 259 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client 16.1.7 Connect: Citrix ICA • Select Connect: Citrix ICA on the control panel and click on the Citrix server to be accessed 16.1.8 Connect: PowerAlert • Select Connect: PowerAlert on the control panel. The PowerAlert software will be launched. 259 - Страница 260 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client 16.2 Advanced Control Panel 16.2.1 System: Terminal Selecting System: Terminal on the control panel logs you in at the command line to the B092-016 Linux kernel. As detailed in Chapters 14 and 15, this enables you to configure and customize your B092-016 using the config and - Страница 261 из 274
Chapter 16: Thin Client 16.3 Remote Control You can access the B092-016 locally via a directly connected keyboard, monitor and mouse (or KVM switch). If the B092016 is connected to a KVMoIP infrastructure, then this may also provide you with some remote access to the B092-016 local consoles (RDP, - Страница 262 из 274
Hardware Specification Appendix A: Hardware Specification FEATURE VALUE Dimensions B096-016 / B096-032 / B096-048: 17 x 12 x 1.75 in (43.2 x 31.3. x 4.5 cm) B092-016: 17 x 6.7 x 1.75 in (44 x 17 x 4.5 cm) B095-004 / B095-003: 4.1x3.4x1.1 in (10.3 x 8.7 x 2.8 cm) B094-008-2E-M-F / B094-008-2E-V: 6.5 - Страница 263 из 274
Serial Port Connectivity Appendix B: Serial Port Connectivity Pinout standards exist for both DB9 and DB25 connectors. However, there are not pinout standards for serial connectivity using RJ45 connectors. Many Console Servers and serially managed servers/ router/ switches/ PSUs have adopted their - Страница 264 из 274
Serial Port Connectivity Connectors included in Console Server All products: DB9F-RJ45S straight connector DB9F-RJ45S cross-over connector 264 - Страница 265 из 274
License Agreement Appendix C: End User License Agreements READ BEFORE USING THE ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE YOU SHOULD CAREFULLY READ THE FOLLOWING TERMS AND CONDITIONS BEFORE USING THE ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, THE USE OF WHICH IS LICENSED FOR USE ONLY AS SET FORTH BELOW. IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO THE TERMS - Страница 266 из 274
License Agreement GOVERNING LAW AND ATTORNEY’S FEES. This EULA is governed by the laws of the State of Utah, USA, excluding its conflict of law rules. You agree that the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods is hereby excluded in its entirety and does not apply - Страница 267 из 274
License Agreement JSch License SDT Connector includes code from JSch, a pure Java implementation of SSH2. JSch is licensed under BSD style license and it is: Copyright (c) 2002, 2003, 2004 Atsuhiko Yamanaka, JCraft, Inc. All rights reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with - Страница 268 из 274
License Agreement 2. You may modify your copy or copies of the Program or any portion of it, thus forming a work based on the Program, and copy and distribute such modifications or work under the terms of Section 1 above, provided that you also meet all of these conditions: a) You must cause the - Страница 269 из 274
License Agreement 6. Each time you redistribute the Program (or any work based on the Program), the recipient automatically receives a license from the original licensor to copy, distribute or modify the Program subject to these terms and conditions. You may not impose any further restrictions on - Страница 270 из 274
License Agreement NO WARRANTY 11. BECAUSE THE PROGRAM IS LICENSED FREE OF CHARGE, THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY - Страница 271 из 274
License Agreement SUN Java License (B092-016 Console Server with PowerAlert product only) 1. Java Technology Restrictions. Licensee shall not create, modify, change the behavior of, or authorize licensees of Licensee to create, modify, or change the behavior of, classes, interfaces, or subpackages - Страница 272 из 274
Service and Warranty Appendix D: Service and Warranty Service Your Tripp Lite product is covered by the warranty described in this manual. A variety of Extended Warranty and On-Site Service Programs are also available from Tripp Lite. For more information on service, visit - Страница 273 из 274
Service and Warranty Product Registration Visit www.tripplite.com/warranty today to register your new Tripp Lite product. You’ll be automatically entered into a drawing for a chance to win a FREE Tripp Lite product!* * No purchase necessary. Void where prohibited. Some restrictions apply. See - Страница 274 из 274