Chapter 13 Spanning Tree Protocol
GS1920 Series User’s Guide
113
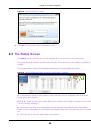
The Switch uses IEEE 802.1w RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) that allows faster convergence
of the spanning tree than STP (while also being backwards compatible with STP-only aware
bridges). In RSTP, topology change information is directly propagated throughout the network from
the device that generates the topology change. In STP, a longer delay is required as the device that
causes a topology change first notifies the root bridge that then notifies the network. Both RSTP
and STP flush unwanted learned addresses from the filtering database. In RSTP, the port states are
Discarding, Learning, and Forwarding.
Note:
In this user’s guide, “STP” refers to both STP and RSTP.
STP Terminology
The root bridge is the base of the spanning tree.
Path cost is the cost of transmitting a frame onto a LAN through that port. The recommended cost
is assigned according to the speed of the link to which a port is attached. The slower the media, the
higher the cost.
On each bridge, the root port is the port through which this bridge communicates with the root. It is
the port on this switch with the lowest path cost to the root (the root path cost). If there is no root
port, then this switch has been accepted as the root bridge of the spanning tree network.
For each LAN segment, a designated bridge is selected. This bridge has the lowest cost to the root
among the bridges connected to the LAN.
How STP Works
After a bridge determines the lowest cost-spanning tree with STP, it enables the root port and the
ports that are the designated ports for connected LANs, and disables all other ports that participate
in STP. Network packets are therefore only forwarded between enabled ports, eliminating any
possible network loops.
STP-aware switches exchange Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) periodically. When the bridged
LAN topology changes, a new spanning tree is constructed.
Once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for Hello BPDUs (Bridge
Protocol Data Units) transmitted from the root bridge. If a bridge does not get a Hello BPDU after a
predefined interval (Max Age), the bridge assumes that the link to the root bridge is down. This
bridge then initiates negotiations with other bridges to reconfigure the network to re-establish a
valid network topology.
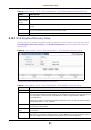
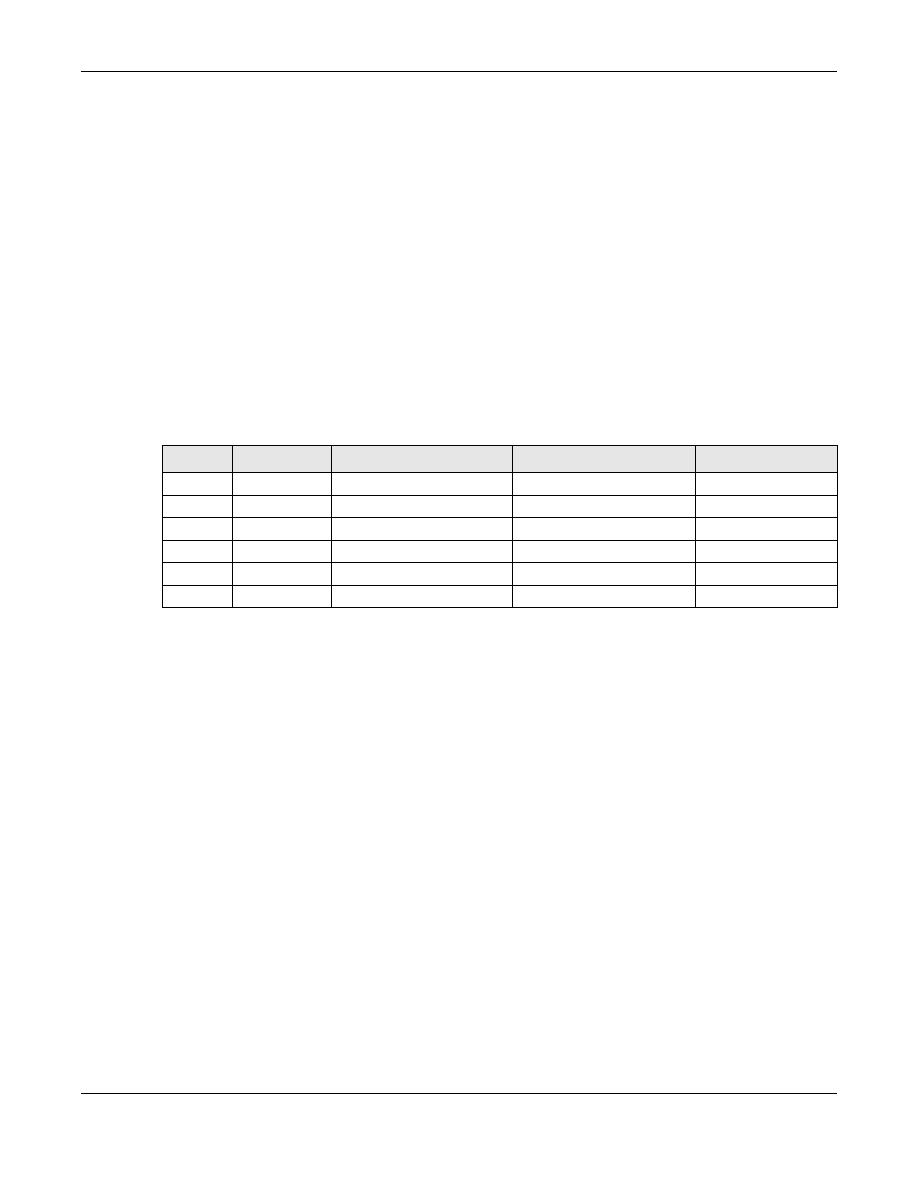
Table 42
STP Path Costs
LINK SPEED
RECOMMENDED VALUE
RECOMMENDED RANGE
ALLOWED RANGE
Path Cost 4Mbps
250
100 to 1000
1 to 65535
Path Cost 10Mbps
100
50 to 600
1 to 65535
Path Cost 16Mbps
62
40 to 400
1 to 65535
Path Cost 100Mbps
19
10 to 60
1 to 65535
Path Cost 1Gbps
4
3 to 10
1 to 65535
Path Cost 10Gbps
2
1 to 5
1 to 65535