Chapter 13 Certificate Screen
NWA1100-N User’s Guide
112
These keys work like a handwritten signature (in fact, certificates are often referred to as “digital
signatures”). Only you can write your signature exactly as it should look. When people know what
your signature looks like, they can verify whether something was signed by you, or by someone
else. In the same way, your private key “writes” your digital signature and your public key allows
people to verify whether data was signed by you, or by someone else. This process works as
follows.
1
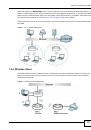
Tim wants to send a message to Jenny. He needs her to be sure that it comes from him, and that
the message content has not been altered by anyone else along the way. Tim generates a public
key pair (one public key and one private key).
2
Tim keeps the private key and makes the public key openly available. This means that anyone who
receives a message seeming to come from Tim can read it and verify whether it is really from him
or not.
3
Tim uses his private key to sign the message and sends it to Jenny.
4
Jenny receives the message and uses Tim’s public key to verify it. Jenny knows that the message is
from Tim, and that although other people may have been able to read the message, no-one can
have altered it (because they cannot re-sign the message with Tim’s private key).
5
Additionally, Jenny uses her own private key to sign a message and Tim uses Jenny’s public key to
verify the message.
13.5.2 Certification Authorities
A Certification Authority (CA) issues certificates and guarantees the identity of each certificate
owner. There are commercial certification authorities like CyberTrust or VeriSign and government
certification authorities. You can use the NWA to generate certification requests that contain
identifying information and public keys and then send the certification requests to a certification
authority.
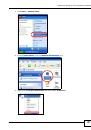
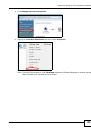
13.5.3 Checking the Fingerprint of a Certificate on Your Computer
A certificate’s fingerprints are message digests calculated using the MD5 or SHA1 algorithms. The
following procedure describes how to check a certificate’s fingerprint to verify that you have the
actual certificate.
1
Browse to where you have the certificate saved on your computer.
2
Make sure that the certificate has a “.cer” or “.crt” file name extension.
Figure 58
Certificates on Your Computer