Appendix D Wireless LANs
NWA1100-N User’s Guide
189
Positioning the antennas properly increases the range and coverage area of a wireless LAN.
Antenna Characteristics
Frequency
An antenna in the frequency of 2.4GHz or 5GHz is needed to communicate efficiently in a wireless
LAN
Radiation Pattern
A radiation pattern is a diagram that allows you to visualize the shape of the antenna’s coverage
area.
Antenna Gain
Antenna gain, measured in dB (decibel), is the increase in coverage within the RF beam width.
Higher antenna gain improves the range of the signal for better communications.
For an indoor site, each 1 dB increase in antenna gain results in a range increase of approximately
2.5%. For an unobstructed outdoor site, each 1dB increase in gain results in a range increase of
approximately 5%. Actual results may vary depending on the network environment.
Antenna gain is sometimes specified in dBi, which is how much the antenna increases the signal
power compared to using an isotropic antenna. An isotropic antenna is a theoretical perfect antenna
that sends out radio signals equally well in all directions. dBi represents the true gain that the
antenna provides.
Types of Antennas for WLAN
There are two types of antennas used for wireless LAN applications.
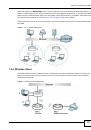
• Omni-directional antennas send the RF signal out in all directions on a horizontal plane. The
coverage area is torus-shaped (like a donut) which makes these antennas ideal for a room
environment. With a wide coverage area, it is possible to make circular overlapping coverage
areas with multiple access points.
• Directional antennas concentrate the RF signal in a beam, like a flashlight does with the light
from its bulb. The angle of the beam determines the width of the coverage pattern. Angles
typically range from 20 degrees (very directional) to 120 degrees (less directional). Directional
antennas are ideal for hallways and outdoor point-to-point applications.
Positioning Antennas
In general, antennas should be mounted as high as practically possible and free of obstructions. In
point-to–point application, position both antennas at the same height and in a direct line of sight to
each other to attain the best performance.
For omni-directional antennas mounted on a table, desk, and so on, point the antenna up. For
omni-directional antennas mounted on a wall or ceiling, point the antenna down. For a single AP
application, place omni-directional antennas as close to the center of the coverage area as possible.