Chapter 23 Multicast
GS2200-24 User’s Guide
192
IP Multicast Addresses
In IPv4, a multicast address allows a device to send packets to a specific group of
hosts (multicast group) in a different subnetwork. A multicast IP address
represents a traffic receiving group, not individual receiving devices. IP addresses
in the Class D range (224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255) are used for IP multicasting.
Certain IP multicast numbers are reserved by IANA for special purposes (see the
IANA web site for more information).
IGMP Snooping
A Switch can passively snoop on IGMP packets transferred between IP multicast
routers/switches and IP multicast hosts to learn the IP multicast group
membership. It checks IGMP packets passing through it, picks out the group
registration information, and configures multicasting accordingly. IGMP snooping
allows the Switch to learn multicast groups without you having to manually
configure them.
The Switch forwards multicast traffic destined for multicast groups (that it has
learned from IGMP snooping or that you have manually configured) to ports that
are members of that group. IGMP snooping generates no additional network
traffic, allowing you to significantly reduce multicast traffic passing through your
Switch.
IGMP Snooping and VLANs
The Switch can perform IGMP snooping on up to 16 VLANs. You can configure the
Switch to automatically learn multicast group membership of any VLANs. The
Switch then performs IGMP snooping on the first 16 VLANs that send IGMP
packets. This is referred to as auto mode. Alternatively, you can specify the VLANs
that IGMP snooping should be performed on. This is referred to as fixed mode. In
fixed mode the Switch does not learn multicast group membership of any VLANs
other than those explicitly added as an IGMP snooping VLAN.
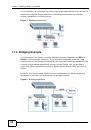
23.1.2.1 MVR Overview
Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) is designed for applications (such as Media-on-
Demand (MoD)) that use multicast traffic across an Ethernet ring-based service
provider network.
MVR allows one single multicast VLAN to be shared among different subscriber
VLANs on the network. While isolated in different subscriber VLANs, connected
devices can subscribe to and unsubscribe from the multicast stream in the
multicast VLAN. This improves bandwidth utilization with reduced multicast traffic
in the subscriber VLANs and simplifies multicast group management.