Prestige 334 User’s Guide
Chapter 5 LAN Screens
68
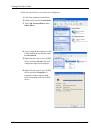
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Third DNS Server
Select
From ISP
if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and
the Prestige's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (read-only)
DNS server IP address that the ISP assigns.
Select
User-Defined
if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS
server's IP address in the field to the right. If you chose
User-Defined
, but leave
the IP address set to 0.0.0.0,
User-Defined
changes to
None
after you click
Apply
. If you set a second choice to
User-Defined
, and enter the same IP
address, the second
User-Defined
changes to
None
after you click
Apply
.
Select
DNS Relay
to have the Prestige act as a DNS proxy. The Prestige's LAN
IP address displays in the field to the right (read-only). The Prestige tells the
DHCP clients on the LAN that the Prestige itself is the DNS server. When a
computer on the LAN sends a DNS query to the Prestige, the Prestige forwards
the query to the Prestige's system DNS server (configured in the
SYSTEM
General
screen) and relays the response back to the computer. You can only
select
DNS Relay
for one of the three servers; if you select DNS Relay for a
second or third DNS server, that choice changes to
None
after you click
Apply
.
Select
None
if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not configure
a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a computer in order to access it.
LAN TCP/IP
IP Address
Type the IP address of your Prestige in dotted decimal notation 192.168.1.1
(factory default).
IP Subnet Mask
The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your
Prestige will automatically calculate the subnet mask based on the IP address
that you assign. Unless you are implementing subnetting, use the subnet mask
computed by the Prestige 255.255.255.0.
RIP Direction
RIP (Routing Information Protocol, RFC1058 and RFC 1389) allows a router to
exchange routing information with other routers. The
RIP Direction
field controls
the sending and receiving of RIP packets. Select the RIP direction from
Both
/
In
Only
/
Out Only
/
None
. When set to
Both
or
Out Only
, the Prestige will broadcast
its routing table periodically. When set to
Both
or
In Only
, it will incorporate the
RIP information that it receives; when set to
None
, it will not send any RIP
packets and will ignore any RIP packets received.
Both
is the default.
RIP Version
The
RIP Version
field controls the format and the broadcasting method of the
RIP packets that the Prestige sends (it recognizes both formats when receiving).
RIP-1
is universally supported but RIP-2 carries more information. RIP-1 is
probably adequate for most networks, unless you have an unusual network
topology. Both
RIP-2B
and
RIP-2M
sends the routing data in RIP-2 format; the
difference being that
RIP-2B
uses subnet broadcasting while
RIP-2M
uses
multicasting. Multicasting can reduce the load on non-router machines since they
generally do not listen to the RIP multicast address and so will not receive the
RIP packets. However, if one router uses multicasting, then all routers on your
network must use multicasting, also. By default, RIP direction is set to
Both
and
the Version set to
RIP-1
.
Multicast
Select
IGMP V-1
or
IGMP V-2
or
None
. IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol)
is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership in a Multicast group - it
is not used to carry user data. IGMP version 2 (RFC 2236) is an improvement
over version 1 (RFC 1112) but IGMP version 1 is still in wide use. If you would
like to read more detailed information about interoperability between IGMP
version 2 and version 1, please see sections 4 and 5 of RFC 2236.
Windows Networking (NetBIOS over TCP/IP): NetBIOS (Network Basic Input/Output System) are TCP
or UDP broadcast packets that enable a computer to connect to and communicate with a LAN. For
some dial-up services such as PPPoE or PPTP, NetBIOS packets cause unwanted calls. However it
may sometimes be necessary to allow NetBIOS packets to pass through to the WAN in order to find a
computer on the WAN.
Table 12
LAN IP
LABEL
DESCRIPTION